Topics in the Chapter
- Basis of Classification
- Phylum Porifera
- Phylum Coelenterata
- Phylum Ctenophora
- Phylum Plathyhelminthes
- Phylum Aschelminthes
- Phylum Annelida
- Phylum Arthropoda
- Phulum Mollusca
- Phylum Echinodermata
- Phyum Hemichordata
- Phylum Chordata
- Division of Vertebrata
- Super-class: Pisces
- Super Class: Tetrapoda
| 1 | Symmetry | : | Distribution of body parts around a | |||||||
| 2 | hypothetical axis. | : | Ostia : Minute pores on body of sponge. | |||||||
| 3 | Osculum | : | Large outlet in body of sponge. | |||||||
| 4 | Hermaphrodite | : | Bisexual. | |||||||
| 5 | Polyp | : | Sessile cylindrical form of coelenterate (Asexual). | |||||||
| 6 | Medusa | : | Umbrella shaped free swimming sexual stage of coelenterate. | |||||||
| 7 | Acoelomate | : | No coelom. | |||||||
| 8 | Pseudocoelom | : | With false coelom (cavity not underlined by mesoderm). | |||||||
| 9 | Dioecious | : | Unisexual. | |||||||
| 10 | Operculum | : | Cover over gills in fish | |||||||
| 11 | Notochord | : | Dorsal rod like bone | |||||||
| 12 | Homoiotherms | : | Warm blooded. | |||||||
| 13 | Bioluminescence | : | Emit light |
-Levels of organisation |
| i) | Cellular level- loose cell aggregates, small division of labour eg. Sponges | |||||||||
| ii) | Tissues grouped into organs eg. | |||||||||
| Coelenterate. | ||||||||||
| iii) | Organ level-Tissues grouped into organs eg. Higher animals. | |||||||||
Circulatory system | ||||||||||
| a) | Open type- No blood vessels, blood flows in sinuses. | |||||||||
| b) | Close type- Blood flows in closed vessels. | |||||||||
Symmetry | 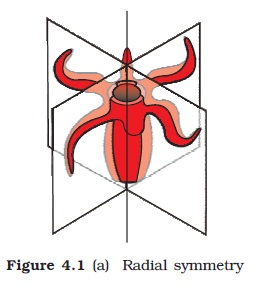 | |||||||||
| - | Asymmetrical – No symmetry eg. Sponges. | |||||||||
| - |  | |||||||||
| - | Radial Symmetry – Any plane passing through central axis divides body in two equal halves. | |||||||||
| - | Bilateral Symmetry – Body can be divided into two equal halves through one plane only. | |||||||||
Diploblastic and Triploblastic organisation – | ||||||||||
| - | Two embryonic layers – Ectoderm and Endoderm – Diploblastic. | |||||||||
| - | Three embryonic layers- Ectoderm, Mesoderm and endoderm- Triploblastic. | |||||||||
Coelom – | ||||||||||
| - | Body cavity lined by mesoderm- True Coelom. | |||||||||
| - | Body cavity not lined by mesoderm Pseudo Coelom. | |||||||||
| - | No body cavity – Acoelomate. | |||||||||
Segmentation – | ||||||||||
| - | True segments- Metameres (Body divided internally and externally). | |||||||||
Notochord – | ||||||||||
| - | With notochord – Chordates. | |||||||||
| - | Without notochord – Non-Chordates. | |||||||||
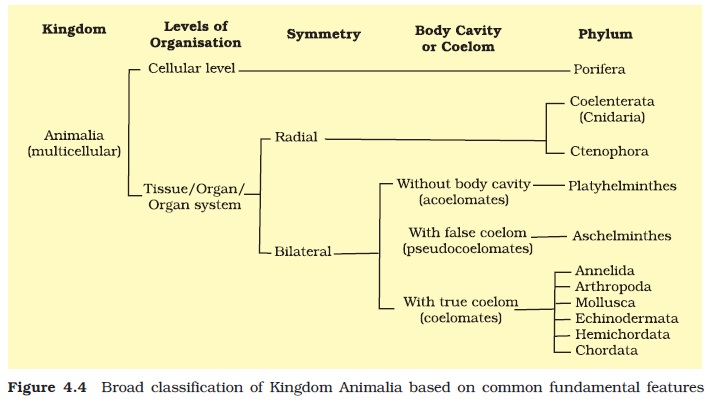
Classification of Animals – | ||||||||||
Phylum Porifera – | ||||
| - | Marine. | |||
| - | Multicellular, cellular grade body. | |||
| - | Asymmetrical. | |||
| - | Water canal system for food, respiration and excretion. | |||
| - | Body wall with many pores – Ostia. | |||
| - | Diploblastic. | |||
| - | Water enters through Ostia and goes out through Osculum. | |||
| - | Skeleton of spicules or spongin fibres. | |||
| - | Hermaphrodite. | |||
| - | Reproduction asexual by fragmentation and sexual by gametes. | |||
| - | Fertilisation is internal, development indirect. | |||
| - | eg. Sycon, Spongilla, Euspongiaetc. | |||
 | ||||
Phylum Coelenterata (Cnidaria) – | ||||
| - | Aquatic (marine), Sessile or free living. | |||
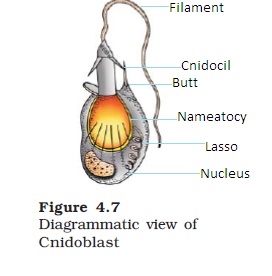
| - | Presence of Cnidoblasts or Cnidocytes – Stinging cells. | |||
| - | Cnidoblasts are for defence, anchorage or predation. | |||
| - | Tissue level body organisation. | |||
| - | Diploblastic. | |||
| - | Central gastro vascular cavity, single opening mouth. | |||
| - | Two body forms – Polyp (Asexual), Medusa (Sexual) stage. | |||
| - | eg Hydra, Physalia, Obelia, Aurelia etc. | |||
 | ||||
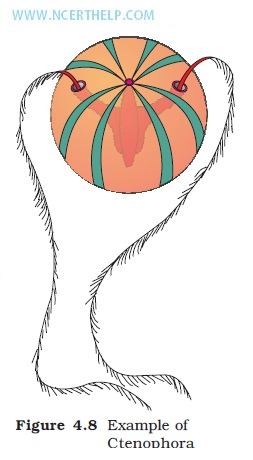
Phylum Ctenophora (sea walnuts or comb jellies) – | ||||
| - | Marine, radial symmetry, Diploblastic, tissue grade. | |||
| - | Eight external rows of Comb Plates. | |||
| - | Bioluminescence. | |||
| - | eg. Ctenoplana, Pleurobrachia etc. | |||
| - | Reproduction sexual. | |||
 | ||||
Phylum Platehelminthes (Flat worms) – | ||||
| - | Body dorsiventrally flattened. | |||
| - | Endoparasite. | |||
| - | Triploblastic, bilateral symmetry. | |||
| - | Acoelomate | |||
| - | -Flame cells- for excretion & osmoregulation. | |||
| - | -Flame cells- for excretion & osmoregulation. | |||
| - | Hermaphrodite | |||
| - | Reproduction – Sexual - Fertilisation internal. | |||
| - | Organ level organisation. | |||
| - | eg. Taeniasolium(Tape worm), Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke). | |||
| Phylum Aschelminthes (Round Worm) – | ||||
| - | Free living or parasitic, aquatic and terrestrial. Bilateral symmetry and Triploblastic. | |||
| - | Pseudocoelomate. Muscular pharynx. | |||
| - | Male smaller and thinner than female. Fertilisation internal, development direct or indirect. | |||
| - | eg. Ascarislumbricoides, Wucherariabancroftiietc. | |||
| Phylum Annelida – | ||||
| - | Aquatic or terrestrial. | |||
| - | Free living or parasitic. | |||
| - | Organ system level body bilateral symmetry and Triploblastic coelomate. | |||
| - | Nephridia for excretion. | |||
| - | Ventral double Nerve cord. | |||
| - | Monoecious or Dioecious. | |||
| - | Reproduction – Sexual. eg. | |||
| - | Earthworm(Pheretima),Nereis etc. | |||
| - | Metameric segmentation. | |||
Phylum Arthropoda( Jointed Legs) – | ||||
| - | Largest phylum. | |||
| - | Bilateral symmetry, Triploblastic, segmented coelomate. | |||
| - | Body - Head, Thorax and Abdomen(three parts). | |||
| - | Blood without haemoglobin and circulatory system open. | |||
| - | Respiration by gills, book lungs and trachea. | |||
| - | Excretion by malpighian tubules. | |||
Phylum Mollusca – | ||||
| - | Soft body animals. Second largest phylum. | |||
| - | Aquatic, bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, coelomate. Body unsegmented divided into head, muscular foot and visceral hump. | |||
| - | Soft mantle over visceral hump. Respiration and excretion through gills. | |||
| - | Unisexual. | |||
| - | Sensory tentacles on head and Radula in mouth. | |||
| - | Oviparous. | |||
| - | -eg.Pila, Octopus etc | |||
PHYLUM ECHINODERMATA | ||||
| - | Body surface spiny, (due to calcareous ossicles) | |||
| - | Marine , organ system level, adult radially symmetrical, triploblastic coelomate. | |||
| Mouth ventral | ||||
| 1 | Water vascular system present for locomotion, capture and transport of food and respiration. | |||
| 2 | Sexes separate fertilization external, development indirect | |||
| - | e.g. Asterias (Starfish), Sea urchin (Echinus), etc. | |||
PHYLUM HEMICHORDATA | ||||
| 1 | Marine | |||
| 2 | Bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, coelomate | |||
| 3 | Body | |||
| i | Proboscis | |||
| ii | Collar | |||
| iii | Trunk | |||
| 4 | Circulatory system open | |||
| 5 | Gills for respiration | |||
| 6 | Proboscis gland for excretion | |||
| Sexes separate fertilization external, development indirect, e.g. Balanoglossus. | ||||
PHYLUM- CHORDATA | ||||
| Distinguishing features | ||||
| 1 | Presence of Notochord | |||
| 2 | Dorsal hollow nerve cord | |||
| 3 | Paired pharyngeal gills slits | |||
| 4 | Post anal tail present | |||
| 5 | Heart is ventral | |||
SUB PHYLA – | ||||
| 1 | Urochordata or Tunicata, Notochord only in larval tail e.g. Ascidia | |||
| 2 | Cephalochordata notochord head to tail in all stage e.g. Branchiostoma | |||
| 3 | Vertebrata: Notochord replaced by a vertebral column. | |||
SUB PHYLUM- VERTEBRATA | ||||
| AGNATHA-without jaw | ||||
| CLASS- Cyclostomata- | ||||
| Ectoparasite on fish | ||||
| - | C ircular mouth | |||
| - | No scales and paired fins | |||
| - | Marine but go in fresh water for spawning and die. Larva returns to ocean. | |||
| - | Eg. Petromyzon, Myxine. | |||
Gnathostomata – with jaws | ||||
| Class - Chondrichthyes | ||||
| - | Aquatic and terrestrial both. | |||
| - | Two pairs of limbs. | |||
| - | No neck. | |||
| - | Body has head and trunk only. | |||
| - | No external ear, tympanum on surface. | |||
| - | Heart three chambered. | |||
| - | Cloaca present. | |||
| - | Respiration by gills, skin and lungs. | |||
| - | Sexes separate. | |||
| - | Fertilisation external, development direc | |||
| - | eg. Ranatigrina, Bufo, Hyla etc. | |||
Class Reptilia – | ||||
| - | Creeping or crawling mode of locomotion. | |||
| - | Skin with scales/scutes. | |||
| - | Tympanum on surface. | |||
| - | Heart three chambered (Four chambered in crocodile). | |||
| - | Fertilisation internal, development direct. | |||
| - | eg. Chelone, Testudo, Naja, Hemidactylus etc. | |||
Class Aves – | ||||
| - | presence of feather, beak and forelimb in form of wing. | |||
| - | Hind limb adapted to clasping, walking and swimming. | |||
| - | No glands on skin (only oil gland at tail base). | |||
| - | Hollow bones (pneumatic). | |||
| - | Air sacs connected to lungs to supplement respiration. | |||
| - | Crop and gizzard are additional chambers in digestive system. | |||
| - | Warm blooded. | |||
| - | Heart four chambered. | |||
| - | Sexes separate. | |||
| - | Fertilisation internal and development direct.eg. | |||
| - | Columba, Psittacula etc. | |||
Class Mammalia – | ||||
| - | Aquatic, terrestrial and aerial. | |||
| - | Mammary glands present for milk production. | |||
| - | Two pairs of limbs. | |||
| - | Skin with hair. | |||
| - | Ear with pinna. | |||
| - | Homoiothermic. | |||
| - | Heart four chambered. | |||
| - | Excretion by kidneys. | |||
| - | .Sexes separate. | |||
Internal fertilisation, vivipary (exception Platypus). | ||||
| - | eg. Whale, Rat , Man, Tiger etc. | |||
| - | Respiration by lungs | |||
Biology Class 11th: Chapter - 4 Animal Kingdom Question Answer




No comments:
Post a Comment