Topics in the Chapter
- Systems of Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Classes of Fungi
- Viruses
- Structure of Virus
- Diseases caused in humans
- Viroids
- Lichens
Revise These Term
1. | Thallus | : | Plant body without true stem, root & Leaf. |
2. | Plankton | : | Organism living in salty areas. |
3. | Halophiles | : | Plants floating passively in water current. |
4. | Chemosynthetic | : | Using chemical reactions as energy source |
5. | Heterotrophic | : | Unable to synthesise own food and dependent on others for food. |
6. | Pathogenic | : | Main body of slime mould. |
7. | Plasmodium | : | Organism feeding on dead & decaying organic matter. |
8. | Saprophyte | : | Organism which depend on living host for food |
9. | Parasite | : | Two organisms living together |
10. | Symbionts | : | benifitting each other. |
11. | Plasmogamy | : | Fusion of cytoplasm. |
1. | Karyogamy | : | Fusion of nuclei. |
2. | Dikaryon | : | A cell with two nuclei. |
3. | Dikaryophase | : | Stage of fungus with dikaryotic cells. |
4. | Isogamous | : | : Morphologically identical gametes |
5. | Anisogamous | : | Morphologically non identical Gametes. |
6. | Oogamous | : | Female gamete oosphere and Male gamete motile. |
Introduction :
1.Aristotle classified organisms for the first time.
2. Two kingdom system includes – Plantae &Animalia.
Objections Against Two Kingdom Classification System
The two kingdom system of classification was accepted for a long time. However, some difficulties arised from this classification as several new living organisms have been discovered.
Some of these difficulties are mentioned below
(a) The first formed organisms were neither plants nor animals.
(b) Fungi do not show similarity with structure, physiology and reproductive system of plants.
(c) It is not easy to recognise the lower organisms as plants or animals. For example, Euglena has mixotrophic (dual) mode of nutrition, while sponges are fixed, branched and irregular creatures like plants.
(d) Slime moulds, a group of fungi, are wall-less in vegetative phase. They develop cell wall in the reproductive phase. Slime moulds can neither be placed in fungi, nor plants.
(e) Lichens are formed by the symbiotic association of an alga and a fungus. They neither resemble plants nor animals.
(f) Prokaryotes do not have an organised nucleus. They have single envelope organisation, absence of spindle apparatus, meiosis and sexual reproduction.
Eukaryotes have a well-defined nucleus, a double envelope organisation, spindle apparatus, meiosis and sexual reproduction.
On the other hand, viruses have no protoplasm and metabolic machinery of their own. Therefore, all of these cannot be kept in a single group.
(g) Unicellular algae like diatoms, euglenoids, dinoflagellates and Protozoa resemble each other.
2. Three Kingdom Classification System
Ernst Haeckel in 1866, classified living organisms into three kingdoms-Plantae, Protista and Animalia. The new kingdom-Protista included all those organisms, which lack the capability of tissue differentiation. These are algae, fungi and Protozoa. Later, kingdom-Protista was reserved only for unicellular organism.
Limitations of Three Kingdom Classification System
Limitations of three kingdom classification are
(a) Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are not separated.
(b) Both unicellular and multicellular organisms are kept in Protista.
3.Four Kingdom Classification System
The four kingdom classification system included Monera in addition to Protista, Plantae and Animalia. Studies with electron microscope made it clear that bacteria and related organisms have a different nuclear structure as compared to others. They are* prokaryotes, thus kingdom-Monera was created by Copeland (1956). Fungi continued to remain with Plantae in this system.
4. Five Kingdom Classification System
This classification was proposed by RH Whittaker, in 1969. Before 1969, the classification systems for the living organisms have undergone several changes overtime.
He created fungi, as separate kingdom.
The main criteria for classification used by Whittaker
(i) Cell structure (ii) Modes of nutrition
(iii) Thallus organisation (iv) Reproduction
(v) Phylogenetic relationships.
Merits of Five Kingdom Classification System
Merits of five kingdom classification system are
(a) Euglena and other transition types which had been included both amongst plants and animals are given proper place under kingdom—Protista.
(b) Fungi have their own biochemical, physiological and structural organisation. They have never been related to plants. In this system of classification fungi are separately placed.
(c) A separate kingdom of prokaryotes include Monera has been created. Monerans differ from all other organisms in their cellular, reproductive and physiological organisations.
(d) The five kingdom classification system is based on cellular organisation, the mode of nutrition and complexity of structure. These were the basic factors used in earliest two kingdom system of classification.
(e) The system shows the gradual evolution of early organisms into plants and animals.
(f) The plant and animal kingdoms are more homogenous than, they were in the two kingdom system of classification.
Demerits of Five Kingdom Classification System
Demerits of five kingdom classification system are
(a) Animal protozoans have been included in kingdom—Protista, which also includes unicellular plants. They show different modes of nutrition.
(b) Yeasts are though, unicellular eukaryotes, do not belong to kingdom—Protista.
(c) Chlorella and Chlamydomonas, though unicellular included under the kingdom-Plantae. They should be kept in Protista.
(d) Euglena like organisms and slime moulds with flexible life style may need the creation of an intermediate kingdom of Protista.
(e) Viruses and viroids are not kept in proper place in this system.
5. Six Kingdom Classification System
It was introduced by Carl Woese a Professor in the Department of Microbiology, University of Illinois in 1990. This system is also named as three domain system as in it organisms are classified into three domains, i.e., Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya.
Kingdom Monera –
1. Prokaryotic unicellular organisms.
2. Most abundant.
3. Also live in extreme habitats viz. Hotsprings, Snow etc. as endoparasite etc.
4. eg. Bacteria.
- Some bacteria are autotrophic others are heterotrophic.
Archaebacteria –
- Cellwall different from other bacteria.
- Live in most harsh habitats eg. Halophile.
- Methanogens are found in the gut of ruminants and produce methane (CH4) gas.
Eubacteria –
- True bacteria.
- Rigid cellwall with or without flagellum.
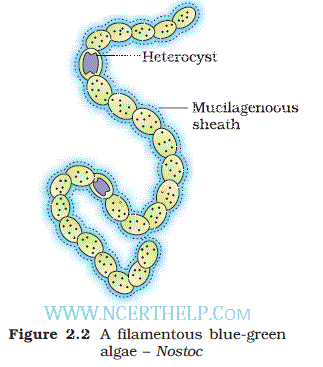
- Cyanobacteria( Blue green algae) are also included in this group.
- Cyanobacteria are Photosynthetic autotrophs, unicellular, colonial or filamentous, with gelatinous sheath.
- Have Heterocyst for N2fixation eg. Nostoc, Anabaena, Oscillatoria, Rivularia, Gloeotrichia etc.
- Mostly bacteria are Heterotrophs and are useful and harmful both to humans.
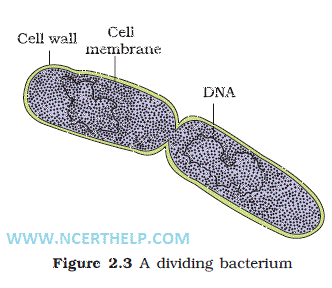
-Reproduction occurs by fission. Also by primitive type of sexual reproduction, by transferring DNA piece from one bacterial cell(+ strain) to other (- strain) (called cell Transduction).
Mycoplasma –
- Smallest unicellular anaerobic organisms having no cellwall.
- Pathogenic in plants and animals.
Kingdom Protista –
- Unicellular eukaryotes.
- Primarily aquatic.
- Some have cilia and flagella.
- Reproduction sexual and asexual both.
Crysophytes –
- Fresh water or marine microscopic Planktons.
- Mostly photosynthetic and cheif producer in ocean eg. Diatomsand Golden algae (Desmids).
- Diatoms with cellwalls in two halves having Silica (indistructible).
- Diatomaceous earth is formed by cellwall deposits of Diatoms and used in polishing, filtration of oils and syrups, fire bricks and explosives.
Dinofagellates –
- Marine.
- Photosynthetic yellow , green, blue, brown or red in colour.
- One longitudinal and other transverse two flagella.
- Gonyaulax causes Red tides.
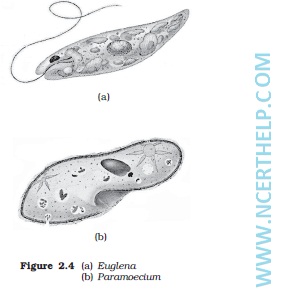
Euglenoids –
- Fresh water forms.
- No cellwall, outer most layer pellicle.
- Two unequal flagella.
- Photosynthetic but also heterotrophic in absence of light ( Mixotroph).
eg. Euglena.
Slime moulds –
- Saprophytes.
- Body is an aggregation called „Plasmodium‟ ( multinucleate, without cellwall, irregular in shape and can spreadover several feet ).
- Plasmodium produces fruiting body having spores with walls which are highly resistant and spread through wind.
Protozoans –
- Fresh water or marine unicellular heterotrophs.
- Primitive relative of animals.strong
(a) Amoeboid Protozoans –
- Free living or parasites.
- Pseudopodia (false feet) formed eg. Amoeba ,Entamoeba.
Flagellated Protozoans –
- Free living or Parasitic with flagella eg.Trypanosoma( causessleeping sickness).
1. Ciliated Protozoans –
- With cilia eg. Paramecium(sleeper animalcule).
(d) Sporozoans –
- Spore like stage in life eg. Plasmodium vivax.
Kingdom Fungi –
- Fungi are a group of achlorophyllous, heterotrophic organisms with cell wall without cellulose.
- Saprophyte or Parasite or Symbiotic.
- Useful and Harmful both.
- Prefer to grow in warm and humid places.
- Unicellular (eg. Yeast) to multicellular filamentous body called mycelium.
- One unit of mycelium called hypha .
- Mycelia maybe coenocytic (no septum) or septate.
- Lichens :– Symbiotic association of fungus and algae.
- Mycorrhiza ;– Symbiotic association of fungi with root of higher plants eg. Pinus.
- Reproduction :–Vegetative : by fragmentation and by spores.Sexual: by gametes.
- Three steps in sexual reproduction
1. Plasmogamy :– fusion of protoplasm.
2 .Karyogamy :- fusion of nuclei.
3. Meiosis of zygote.
Phycomycetes –
- Grow on aquatic places or decaying wood or damp places or obligate parasite.
- Mycelium aseptate, coenocytic.- Reproduction - asexual by zoospores or aplanospores. Sexual by zygospores.
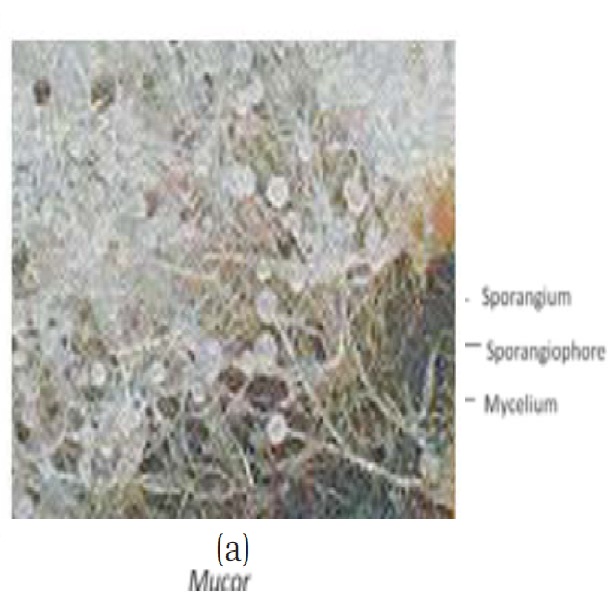

Ascomycets (sac fungi)-
-Unicellular (eg. Yeast) or multicellular
-Saprophytic or parasitic.
-Maybe coprophillus (growing on dung) eg. peziza.
-Mycelium septate and branched.
-Reproduction – asexual by exogenously produced conidia.
-sexually by Ascospares produced in asci present in fruiting body called Ascocarp.
-egAspergillus, Claviceps, Neurospora, Saccharomyces (yeast) etc.
.jpg)
Basidiomycetes (club fungi) –
- Grow on soil , logs or parasites ( rusts and smuts).
- Mycelium septate and branched and of two types
- Uninucleate 2) Dikaryophase.
- Reproduction – vegetative by fragmentation sexualby two somatic cells giving rise to Dikaryophase.
- Dikaryophase makes fruiting body Basidiocarp having Basidia.
- Inside basidia (singular basidium)
- Karyogamy and meiosis occours.
- Meiosis results in formation of four basidiopores.
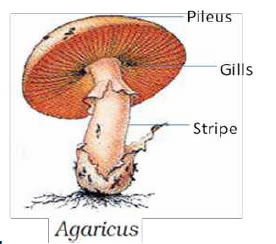
eg. Agaricus (mushroom), Ustilago (smut fungi), Puccinia (rust fungus).
Deuteromycetes (Fungi- imperfectil) –
- It is formed class – Group of Fungi whose complete life cycle is not known.-Saprophyte/parasite , mostly decomposers.- eg. Alternaria, colletotrichum, Trichoderma.
Kingdom Plantae –
- Eukaryotic, chlorophyll bearing autotrophic organisms.
- Only few members partialheterotrophs eg. Insectivorus plants (Bladder wort and Venus flytrap).
- Few parasites eg. Cuscuta
- Reproduction – vegetative,asexual and sexual.
- Life cycle shows alternation of generation.
- eg. Algae, Bryophytes,Pteridophyte, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
Kingdom Animalia –
- Eukaryotic, Heterotrophic organisms.
- No chloroplast and no cell wall.
-Holozoic mode of nutrition
- Definite shape and size and capable of locomotion.
Reproduction
- sexual in general
- eg. frog, cockroach, cow, man etc.
- Viruses, Viroids and Lichens
- Viruses Connecting link between living and non living.
- Non cellular structure consisting of protein coat and Nucleic acid
- Can reproduce within a host cell.
- Host cell may be killed.
- Viruses which infect bacteria are called Bacteriophage.
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)-
- Protein coat: - capsid consists of capsomers.
- Viruses can cause diseases viz. Mumps, Small pox, Herpes, Influenza, AIDS etc.

![]()
Viroids
- Free RNA without protein coat.
Lichens
- Composite organisms.
-Symbiotic association between Algae (Phycobiont),Fungi (Mycobiont).




No comments:
Post a Comment